September 2024 Drug Safety Updates: drug-induced liver injury and Zeposia, insulin medication errors, 6 more
Consumer-friendly summaries of new safety information added to FDA drug labels
Docetaxel (docetaxel)
Docetaxel is a chemotherapy drug used to treat various kinds of cancer. It is also known under Taxotere brand name. The label warns that animal studies have shown that Docetaxel Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Females of reproductive potential are advised to use effective contraception during treatment and for 2 months after the last dose of Docetaxel Injection. Male patients taking Docetaxel with female partners of reproductive potential are advised to use contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose.
FDA Safety Label Change Docetaxel
Fosrenol (lanthanum carbonate)
Fosrenol is available as a chewable tablet or powder formulation and is used to lower phosphate levels in patients with end stage kidney disease. The label was updated to warn against using it if patients have an allergy or hypersensitivity to (lanthanum carbonate) or any ingredient in the formulation.
FDA Safety Label Change Fosrenol
Gloperba (colchicine)
Gloperba is a ready-to-use cherry-flavored oral solution taken daily to prevent gout flare-ups in adults. Its label was updated to add warnings about muscle-related side effects:
Concomitant use of atorvastatin, simvastatin, pravastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, rosuvastatin, gemfibrozil, fenofibrate, fenofibric acid or benzafibrate (themselves associated with myotoxicity) or cyclosporine with GLOPERBA may potentiate the development of myopathy. (muscle pain)
Once colchicine is stopped, the symptoms generally resolve within one week to several months. Patients with both liver and kidney problems are advised not to take Gloperba.
FDA Safety Label Change Gloperba
Prevymis (letermovir)
Prevymis oral and intravenous formulation is taken to prevent post-transplant (kidney and bone marrow) infection. The label was updated to include guidelines and risks for pediatric use in patients 12 years and older and for cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and disease in adults and children (age 6 months and up).
FDA Safety Label Change Prevymis
Roszet (ezetimibe; rosuvastatin calcium)
Roszet is a statin drug used to reduce cholesterol. A section of the revised label outlines steps to prevent or reduce the risk of myopathy (muscle pain) and rhabdomyolysis (muscle tissue death). The label now warns of rare reports of liver failure, increase in liver enzyme levels, and immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), which is an autoimmune muscle disease. Clinical trials information was updated.
FDA Safety Label Change Roszet
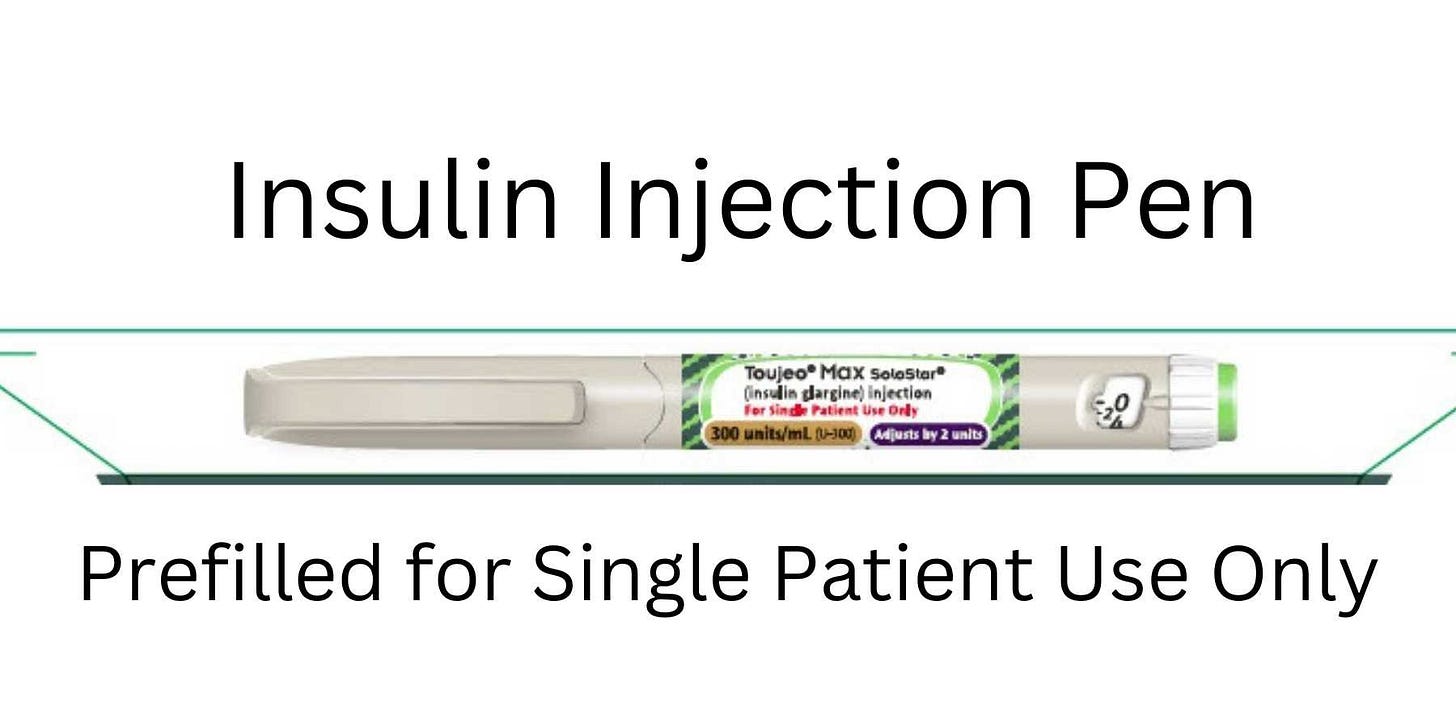
Toujeo Max Solostar and Toujeo Solostar (insulin glargine recombinant)
Toujeo Max Solostar and Toujeo Solostar are synthetic, concentrated, long-acting insulin used to treat diabetes mellitus (Type 1 or Type 2) in children and adults. It works by helping blood sugar (glucose) get into cells so your body can use it for energy. The label was updated to warn of the risk of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia due to potential medication errors:
Inform patients that TOUJEO contains 300 units of insulin glargine per mL (U-300) compared to formulations of insulin glargine that contain 100 units/mL (U-100). To avoid dosing errors and potential overdose, instruct patients to never use a syringe to remove TOUJEO from the TOUJEO SoloStar or TOUJEO Max SoloStar single-patient-use prefilled pen.
The dose counter of TOUJEO SoloStar or TOUJEO Max SoloStar single- patient-use prefilled pen shows the number of units of TOUJEO to be injected and no dose recalculation is required.
Another popular insulin glargine product, Lantus, is an example of a formulation that contains 100 units per mL.
FDA Safety Label Change Toujeo Max Solostar
FDA Safety Label Change Toujeo Solostar
Patient reviews of Toujeo Solostar
Velphoro (sucroferric oxyhydroxide)
Velphoro helps control phosphorus levels in people with kidney failure who are on dialysis. It is a chewable tablet that should be taken with meals and may cause diarrhea or darker stools because it contains iron. The new warning alerts patients that gastrointestinal bleeding may be masked by stool discoloration.
FDA Safety Label Change for Velphoro
Zeposia (ozanimod hydrochloride)
Zeposia treats multiple sclerosis (MS) and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) in adults. The label update warns that its use with other medicines, including monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (such as selegiline, phenelzine, linezolid) can cause serious side effects. The label update also warns that patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of drug-induced liver injury:
Clinically significant liver injury, including acute liver failure requiring transplant, has occurred in patients treated with ZEPOSIA in the postmarketing setting. Signs of liver injury, including elevated serum hepatic enzymes and elevated total bilirubin, have occurred as early as ten days after the first dose.
Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels, if not recently available (i.e., within 6 months), before initiation of ZEPOSIA. Obtain transaminase levels and total bilirubin levels periodically during treatment and until two months after ZEPOSIA discontinuation.
If patient experiences symptoms of liver injury, including unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or jaundice and/or dark urine, they should have hepatic enzymes promptly checked, and ZEPOSIA should be interrupted. Treatment should not be resumed if a plausible alternative etiology for the signs and symptoms cannot be established, because these patients are at risk for severe drug-induced liver injury.
Also, a newly added subsection identifies adverse reactions identified during post-approval use of Zeposia.
FDA Safety Label Change for Zeposia
To learn more about your medicine and whether it might cause liver injury, look it up in the LiverTox database, produced by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). This online publication is regularly updated and contains more than 1,000 prescription and over-the-counter medications and herbal and dietary supplements. Each drug has a separate article that discusses the potential for liver toxicity, how long it takes for liver injuries to happen, and how soon or how well the condition resolves after time passes or after the medication is stopped. Many entries also include case studies. While the information is technical, it is written for both patients and physicians.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547852/
Because of our upcoming special safety-related report on the discontinuation of TIRF (Transmucosal Immediate-Release Fentanyl) pain medications, the regular “Drugs & Treatments” News will be sent on Tuesday, September 10.
Visit us at www.askapatient.com for drug ratings and more news!

