Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Manufacturing for U.S. Drugs: Maps & Data
Improving Drug Safety in 2023
Inspecting the quality of hundreds of overseas pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities is not an easy task for the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). In 2018, just 22 FDA staff were present in China. By 2020, when the Covid-19 outbreak began, U.S. personnel left the country and in-person inspections stopped completely. Onsite inspections did not begin again until April 2023, according to a Congressional Subcommittee on Health Report.
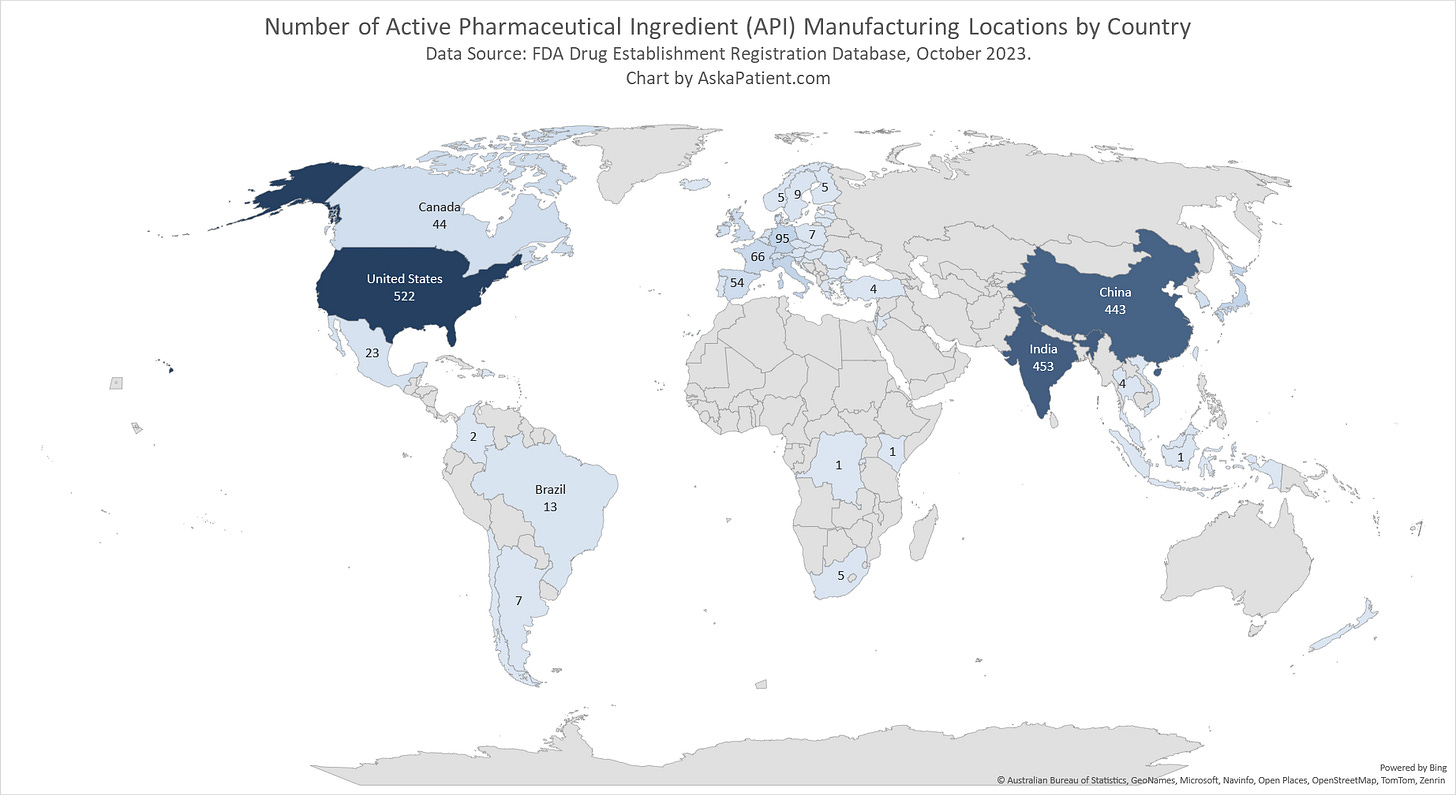
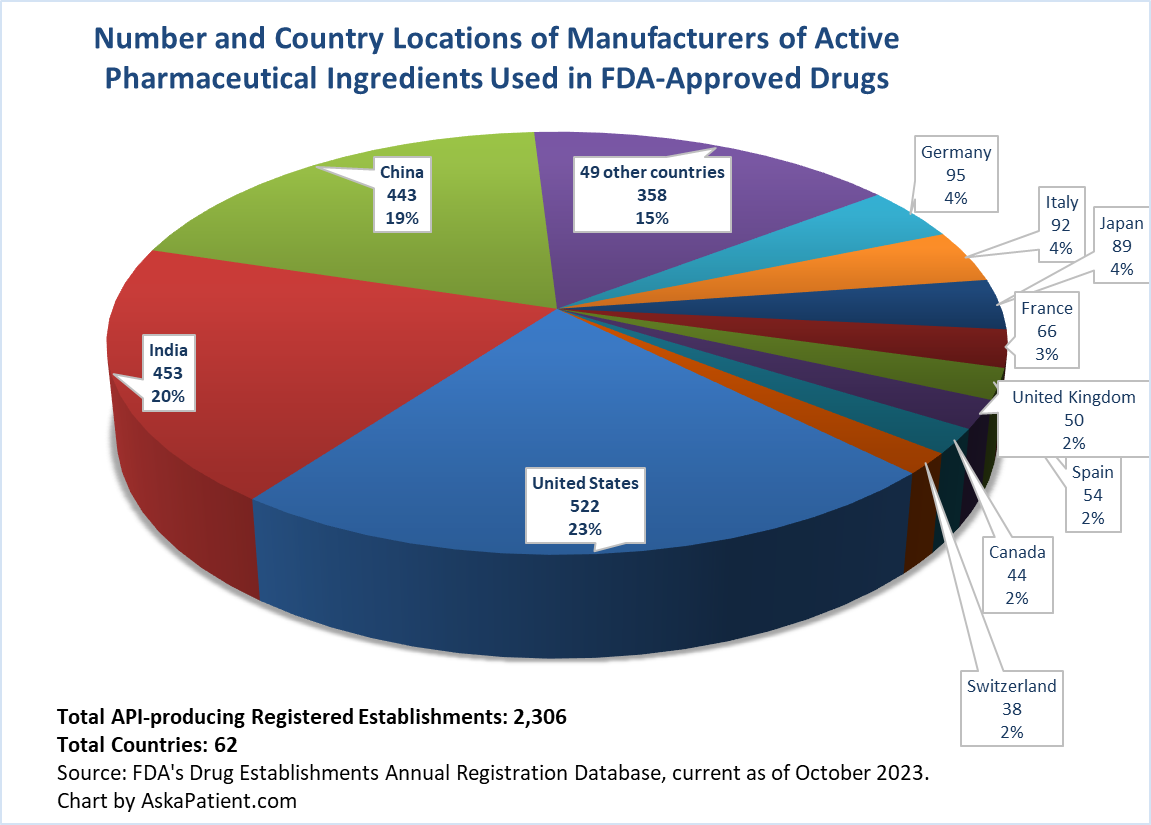
Even though about 40% of registered Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) manufacturing facilities are located in China or India, the share of total production supply from those facilities is much greater. CNBC reports that about 80% of the APIs used in U.S. drugs come from facilities in China and India. Rosemary Gibson, author of “China Rx: Exposing the Risks of America's Dependence on China for Medicine,” estimates that India also relies heavily on China for key starting materials to make APIs. She estimates that China controls 80 to 90 percent of these key starting materials.
https://www.politico.eu/article/europe-china-medicines-drug-imports-health/?aid=app_feed
Drug safety concerns, including recent recalls and shortages due to quality problems, have put a spotlight on drug manufacturing practices. Here are some recent concerns and actions by oversight committees in Congress along with FDA steps taken to address quality safety concerns and shortages.
- In July 2023, the House Energy and Commerce Committee Republicans sent a letter to FDA Commissioner Robert Califf raising questions regarding the FDA's insufficient foreign drug inspections in India and China.
- In September 2023, the FDA issued new guidance on how the agency intends to use alternative tools in advance or in lieu of an inspection to remotely evaluate drug manufacturing facilities named in pending applications as part of FDA’s drug review process. FDA uses a risk-based approach to determine if alternative tools, including requesting records from manufacturers, remote interactive evaluations of facilities, and receiving information from foreign regulatory partners, may be used.
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-issues-guidance-using-remote-oversight-tools-help-approve-drugs
- On November 2, 2023, the House Committee on Oversight and Accountability sent a letter to the FDA with concerns about drug shortages, requesting documents and insights on how the agency is handling supply chain issues. The letter also states that supply chain issues have been going on long before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Apart from pandemic supply chain delays, the committee cites over-reliance on offshore manufacturing facilities, surging demand for pharmaceuticals, and diminishing manufacturing of generics. In an attempt to ease the shortages, the FDA temporarily authorized imports of cancer drugs produced by non-FDA approved Chinese manufacturers earlier this year.
https://www.pharmexec.com/view/congress-launches-investigation-into-fda-drug-shortage-response
- In November 2023, FDA commissioner Robert Califf wrote about his October 2023 trip to India, including the capital city of New Delhi and the pharmaceutical and technology hub Hyderabad. According to the FDA drug establishments database, 32 API manufacturing establishments are registered in Hyderabad.
Califf said that both manufacturing systems quality and concerns with the conduct of clinical trials performed in support of drug applications have caused safety problems for drugs dispensed in the U.S. However, Califf said that "the discussions on my trip reflected a continued willingness and enthusiasm from the Government of India and industry alike to work collaboratively with the FDA to ensure robust quality management for safe and effective drugs."
https://www.fda.gov/news-events/fda-voices/indias-unique-opportunity-and-important-responsibility-pharmacy-world
Maps of API Manufacturing Establishments Locations (as of October 2023):
Research Resources:
While the number of FDA-registered API establishments worldwide increased from 1,996 to 2,306 between 2019 and 2023, the distribution of the locations of them are about the same compared with four years ago. The article linked below, with a focus on valsartan recalls that began in 2018, provides 2019 API establishment data. Note that the U.S. went from having 415 registered establishments to 522 registered establishments in 2023. Some of the newly registered establishments in the U.S. are cannabis API locations (as indicated by the name of some of the registered companies), but this needs further analysis to find out if it’s a significant reason for the increase or if there are other factors at play.
https://www.askapatient.com/news/generic-api-valsartan-worldwide-recall.asp
Database of FDA Inspections:
https://datadashboard.fda.gov/ora/cd/inspections.htm
FDA Drug Establishment Database:
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/drug-establishments-current-registration-site
FDA 2022 CDER Office of Pharmaceutical Quality Annual Report
https://www.fda.gov/media/165352/download?attachment
The FDA is establishing a program to promote quality management maturity (QMM) at drug manufacturing establishments that go beyond current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) requirements.
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/pharmaceutical-quality-resources/cder-quality-management-maturity